Factors Influencing Bathroom Vanity Drain Pipe Size

Choosing the right drain pipe size for your bathroom vanity is crucial for ensuring proper drainage and preventing clogs. Several factors come into play when determining the appropriate pipe size, and understanding these factors is essential for making an informed decision.
Vanity Sink Size and Design
The size and design of your vanity sink directly influence the drain pipe size you need. Larger sinks, especially those with multiple bowls, require larger drain pipes to accommodate the increased water flow. Similarly, sinks with complex designs, such as those with multiple drain holes or integrated overflow features, may necessitate larger pipes to handle the water volume efficiently.
Standard Drain Pipe Sizes for Bathroom Vanities: What Size Drain Pipe For Bathroom Vanity
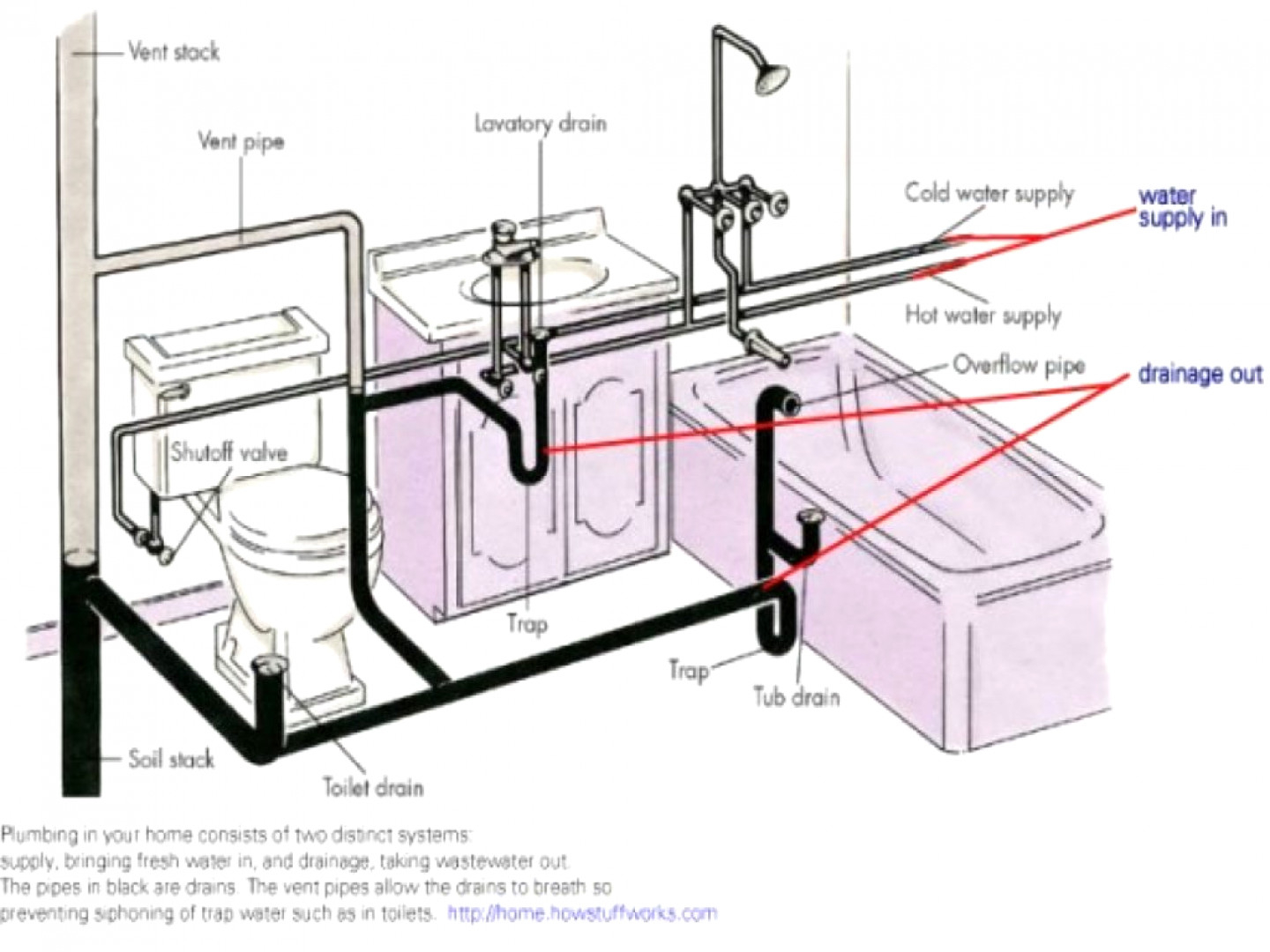
Determining the correct drain pipe size for your bathroom vanity is crucial for ensuring proper water flow and preventing clogs. A well-sized drain pipe effectively carries wastewater away from the sink, maintaining a smooth and efficient plumbing system.
Standard Drain Pipe Sizes for Bathroom Vanities
The standard drain pipe size for a bathroom vanity depends on the sink size, fixture type, and flow rate. Here’s a comprehensive table outlining the standard drain pipe sizes:
| Sink Size | Fixture Type | Flow Rate (GPM) | Drain Pipe Size (inches) | Small (18" – 24") | Single-bowl sink | 1.5 – 2.0 | 1 1/2 | Medium (24" – 30") | Double-bowl sink | 2.0 – 2.5 | 1 1/2 | Large (30" – 36") | Single-bowl sink | 2.5 – 3.0 | 2 | Extra Large (36" – 42") | Double-bowl sink | 3.0 – 3.5 | 2 |
|---|
Note: The flow rate is the amount of water that flows through the faucet per minute. The drain pipe size should be large enough to handle the flow rate of the faucet.
Visual Representation of Drain Pipe Sizes
To better understand the visual representation of drain pipe sizes, imagine a circular pipe with a diameter of 1 1/2 inches. This diameter represents the standard size for most bathroom vanity drains. A larger diameter, such as 2 inches, is used for vanities with higher flow rates or larger sinks.
Measuring the Diameter of Existing Drain Pipes
To accurately measure the diameter of an existing drain pipe, follow these steps:
1. Clean the pipe: Use a cleaning cloth or brush to remove any debris or dirt that might obstruct your measurement.
2. Use a measuring tape: Wrap the measuring tape around the pipe’s circumference, ensuring it goes around the widest part of the pipe.
3. Divide the circumference by pi: Divide the circumference measurement by 3.14159 (pi) to calculate the diameter.
For example, if the circumference of the pipe is 4.71 inches, the diameter would be approximately 1.5 inches (4.71 / 3.14159 = 1.5).
Installation Considerations and Best Practices
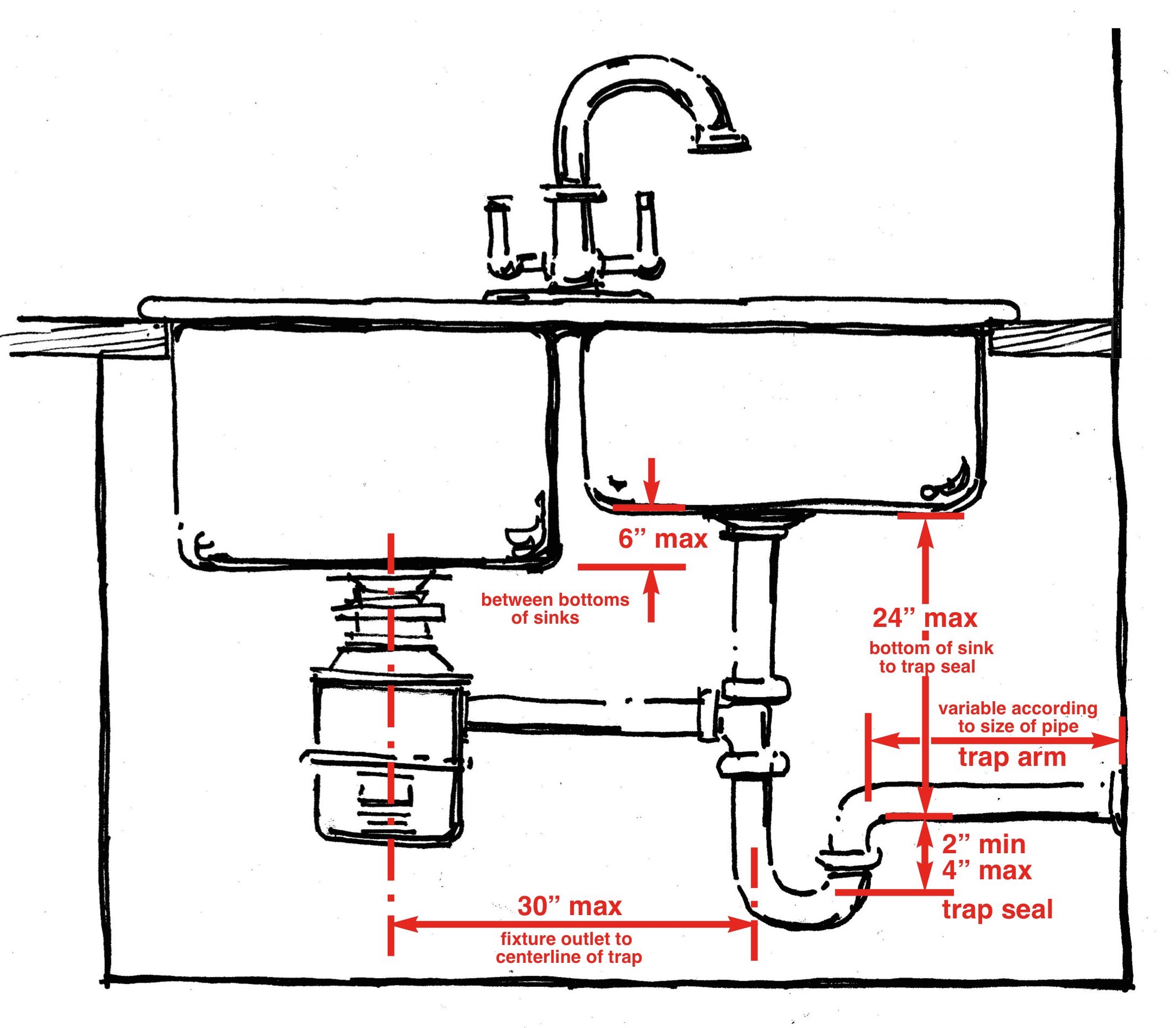
Installing a bathroom vanity drain pipe correctly is crucial for preventing leaks, ensuring proper drainage, and maintaining a functional bathroom. This process involves careful planning, selecting the right materials, and following specific installation steps.
Tools and Materials Needed for Installation
The following tools and materials are essential for installing a bathroom vanity drain pipe:
- Drain pipe cutter
- Pipe wrench
- Channel-lock pliers
- Level
- Measuring tape
- Utility knife
- Plumber’s putty
- Teflon tape
- PVC cement
- PVC primer
- Drain pipe (PVC or ABS)
- Traps (P-trap, S-trap, or J-trap)
- Fittings (elbows, tees, couplings, etc.)
- Vent pipe (if required)
- Drain strainer
- Safety glasses and gloves
Step-by-Step Guide for Installing a Bathroom Vanity Drain Pipe
- Plan the Drain Pipe Route: Determine the shortest and most efficient path for the drain pipe from the vanity to the main drain line. Consider any obstacles or existing plumbing that may affect the route.
- Cut and Connect the Drain Pipe: Measure and cut the drain pipe to the required length. Use a drain pipe cutter to ensure clean and precise cuts. Connect the drain pipe to the vanity using the appropriate fittings, ensuring a secure and leak-free connection.
- Install the Trap: Install the trap (P-trap, S-trap, or J-trap) to prevent sewer gases from entering the bathroom. Ensure the trap is properly sealed and connected to the drain pipe.
- Connect to the Main Drain Line: Connect the drain pipe to the main drain line using the appropriate fittings. Ensure the connection is secure and watertight.
- Vent the Drain Pipe: If required by local plumbing codes, install a vent pipe to prevent siphoning and ensure proper drainage. The vent pipe should extend above the roofline and connect to the drain pipe using a vent stack fitting.
- Test for Leaks: Once the installation is complete, test for leaks by running water through the vanity drain. Carefully inspect all connections for leaks and tighten any loose fittings.
Importance of Using Appropriate Fittings and Connections, What size drain pipe for bathroom vanity
Using appropriate fittings and connections is crucial for ensuring a leak-free and durable drain pipe installation.
- Secure Connections: Fittings and connections should be properly secured to prevent leaks. Use plumber’s putty or Teflon tape to seal threaded connections, and PVC cement for solvent-welded connections.
- Proper Fit: Fittings should fit snugly and securely to the drain pipe to prevent leaks. Avoid using fittings that are too large or too small, as this can lead to leaks or blockages.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the fittings and drain pipe are compatible with each other. For example, PVC fittings should be used with PVC drain pipe, and ABS fittings should be used with ABS drain pipe.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Drain Pipe Installation Methods
There are different methods for installing a bathroom vanity drain pipe, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Solvent Welding: Solvent welding is a common method for connecting PVC drain pipe. It involves using PVC cement and primer to create a strong and durable bond between the pipe and fittings.
- Advantages: Solvent welding provides a strong and durable connection that is resistant to leaks. It is also a relatively easy and fast method of installation.
- Disadvantages: Solvent welding requires careful preparation and handling of the PVC cement and primer. It can also be difficult to remove or adjust a solvent-welded connection once it has been made.
- Threaded Connections: Threaded connections are often used for connecting metal drain pipe. They involve using threaded fittings and pipe dope or Teflon tape to create a secure connection.
- Advantages: Threaded connections are relatively easy to assemble and disassemble, making them convenient for repairs or adjustments. They are also suitable for use with both metal and plastic drain pipe.
- Disadvantages: Threaded connections can be prone to leaks if they are not properly sealed. They can also be more time-consuming to install than solvent-welded connections.
